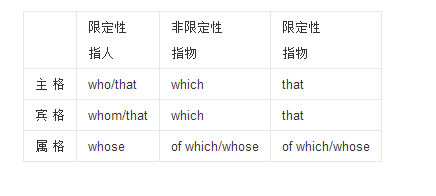
指针与数组的关系是什么啊
的有关信息介绍如下:1、指针:系统为某一个变量开辟单元格,指针便指向此单元格的变量值。
2、数组:系统为某一组数开辟一组单元格,数组首地址便是你定义的数组变量名。
数组和指针的唯一区别是,不能改变数组名称指向的地址。
对于数组来说,数组的首地址,也可以用指针来表示操作,如:
int a[10];
int *p,n;
p = a;
对第一个元素取值,可以用几种方法:
n =a[0];
n = *p;
n = p[0];
n = *(p+0) ;
但是以下语句则是非法的:
readings = totals; // 非法!不能改变 readings totals = dptr; // 非法!不能改变 totals
数组名称是指针常量。不能让它们指向除了它们所代表的数组之外的任何东西。

扩展资料
下面的程序定义了一个 double 数组和一个 double 指针,该指针分配了数组的起始地址。随后,不仅指针符号可以与数组名称一起使用,而且下标符号也可以与指针一起使用。
int main()
{
const int NUM_COINS = 5;
double coins[NUM_COINS] = {0.05, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0};
double *doublePtr; // Pointer to a double
// Assign the address of the coins array to doublePtr
doublePtr = coins;
// Display the contents of the coins array
// Use subscripts with the pointer!
cout << setprecision (2);
cout << "Here are the values in the coins array:\n";
for (int count = 0; count < NUM_COINS; count++)
cout << doublePtr [count] << " ";
// Display the contents of the coins array again, but this time use pointer notation with the array name!
cout << "\nAnd here they are again:\n";
for (int count = 0; count < NUM_COINS; count++)
cout << *(coins + count) << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
程序输出结果:
Here are the values in the coins array: 0.05 0.1 0.25 0.5 1 And here they are again: 0.05 0.1 0.25 0.5 1
当一个数组的地址分配给一个指针时,就不需要地址运算符了。由于数组的名称已经是一个地址,所以使用 & 运算符是不正确的。但是,可以使用地址运算符来获取数组中单个元素的地址。